Eggs can be part of a good breakfast, a healthy snack, or a fulfilling dinner depending on the way you make them. There are many ways to prepare eggs; they can be boiled, fried, poached, scrambled, and much more. Omelets are made by beating eggs and cooking them with oil or butter in a frying pan. We know that eggs are healthy, but are omelets healthy?
Read on to find out.
Are Omelets Healthy for You?
Omelets are usually fried in a teaspoon of oil or butter. So, are omelets healthy for you? Yes, they are if you add sufficient vegetables and use less oil.
Here are some omelet benefits:
1. Good source of proteins
One large omelet contains six grams of proteins. Consuming a protein-rich breakfast that includes an omelet is a good option.
According to a study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, people who eat a high-protein breakfast feel full for a longer time compared to those who have a low-protein breakfast.
2. Prevents cravings
Another study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition analyzed ghrelin production. Ghrelin is the appetite hormone that stimulates hunger. The study found that a high-protein breakfast decreases ghrelin secretion to a greater extent than a high-carbohydrate breakfast.
A high-protein breakfast reduces gastric emptying. Protein is essential for almost all our body’s functions such as tissue repair, bone health, enzyme and hormone secretion, and more.
So, eating an omelet will keep you satisfied and energized for a longer time. Indirectly, omelets help with weight loss by preventing cravings.
3. Supports brain health
Eggs contain choline, an essential nutrient that is important for nerve function and brain health. Eggs also have a good amount of a vital mineral called selenium. It combats free radicals that damage cells.
4. Good for bodybuilding
We know that hard-boiled eggs are good for bodybuilding. Eggs have omega-3 fatty acids and anti-inflammatory properties.
Boiled eggs can be eaten on their own or chopped and tossed into a salad. Omelets are a good switch when you get bored of boiled eggs. But, are omelets good for bodybuilding? Omelets have all the vitamins and minerals present in hard-boiled eggs.
Omelets are good for bodybuilding if consumed in moderation. To make omelets, crack eggs into any fat such as butter, bacon grease, or vegetable oil. You can opt for a low-fat omelet by choosing an appropriate oil and its quantity.
To increase the protein content and enhance the flavor, you can add meat or plant proteins. Some ingredients which you can add include diced chicken, quinoa, shrimp, or black beans.
Is an omelet healthy for dinner? Well, of course, it will depend on the method of preparation. A healthy and nourishing omelet that includes fresh vegetables can be a filling dinner, but you should limit your intake as eggs have cholesterol.
Consuming a three-egg omelet for dinner is not healthy. It will increase the calorie and fat content. However, adding vegetables such as peppers, onions, mushrooms, and tomatoes will boost the nutrient content of the omelet.
An omelet’s nutritional value will also depend on whether you use whole eggs or only the whites. One fried egg has 90 calories, so a three-egg omelet will contain 270 calories! However, if you leave out the yolk, you would be leaving out many nutrients such as proteins, vitamin B12, selenium, and more.
If you want to have an omelet for dinner, eat it at least two to three hours before you go to sleep. Also, instead of three eggs, use only one or two whole eggs. Avoid cheese and add lots of vegetables. You can eat it with a whole grain bread slice.
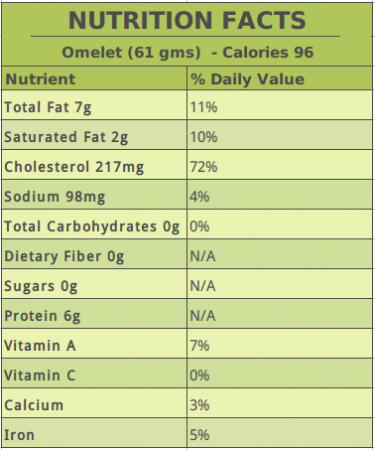
Omelet Nutrition Facts
An omelet made with a whole egg contains a good amount of proteins, vitamins A, D, B, and K, omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, selenium, phosphorus, and other nutrients in trace amounts.
Omelet Nutrition Chart
Omelets are ideal for vegetarians who eat eggs because there aren’t many food sources containing vital nutrients such as vitamin B12 and vitamin D except for dairy products.
Omelet vs. Boiled Egg
Are omelets more healthy compared to boiled eggs? As previously mentioned, eggs are a good source of proteins. According to a study published in the British Journal of Nutrition, healthy people can eat eggs daily.
Eggs don’t increase the risk of heart disease. As we said before, the way an egg is prepared will affect the calorie and the fat content. An egg contains 210 milligrams of cholesterol. However, the cholesterol content is independent of the method of preparation.
One large hard-boiled egg contains 77 calories. An omelet contains 90 calories. A hard-boiled egg provides five grams of fats, two grams of which are saturated.
An omelet provides seven grams of fats, out of which two grams are saturated. Frying or boiling doesn’t affect the vitamin and mineral content to a vast extent.
Fried egg and boiled egg have similar nutrient profiles. The major difference is in the fat content through the oil or butter used. Both egg preparation methods provide the same amount of proteins, which is six grams. However, omelets have a higher iron content than boiled eggs.
Omletes are healthy if we don’t take into consideration the fat content. You can easily eat one egg or omelet a day and reap its health benefits.
Healthy Omelet Recipes
Here are couple of healthy omelet recipes you can try for breakfast.
Open-Faced Pastrami Omelet Recipe
Ingredients:
- 1 ½ cups of sliced peeled English cucumber
- 1 tablespoon of Dijon mustard
- 3/8 teaspoon of ground black pepper, divided
- 2 tablespoons of chopped fresh dill
- 6 large eggs, beaten
- 3 ounces of chopped pastrami
- 3 green onions, sliced
- 1 tablespoon of cider vinegar
- ½ teaspoon of prepared horseradish
- ¼ teaspoon of salt, divided
- 2 teaspoons of olive oil
- 4 large lettuce leaves
- 4 (1-ounce) slices pumpernickel bread, toasted
Directions
In a bowl, combine cucumber, vinegar, mustard, horseradish, 1/8 teaspoon salt, and 1/8 teaspoon pepper. Let the mixture stand for 10 minutes.
In another bowl combine remaining 1/8 teaspoon salt, remaining ¼ teaspoon pepper, eggs, dill, pastrami, and onions. Whisk it gently.
Over medium heat, heat a nonstick skillet and grease it with oil. Add the beaten eggs and cook for two minutes. Reduce the heat and cook covered until it sets.
Cut the omelet into four wedges. Place a lettuce leaf on each bread slice. Top it with one omelet wedge. Spread ¼ cup of cucumber mixture and serve.
Mushroom and Spinach Omelet Recipe
Ingredients:
- 1 tablespoon of extra-virgin olive oil
- ½ cup of chopped shallots
- 1 thyme sprig
- 6 ounces of fresh baby spinach
- 3 garlic cloves, minced
- 1 (8-ounce) package of sliced white mushrooms
- ¾ teaspoon of kosher salt, divided
- 1 tablespoon of butter, divided
- ³⁄8 teaspoon of ground black pepper, divided
- 8 large eggs, divided
Directions
Heat oil in a nonstick skillet. Add garlic, shallots, mushrooms, and thyme. Saute for few minutes or until the mushrooms turn brown. Add spinach and saute until the liquid evaporates.
Remove the mixture from pan. Discard the thyme sprig. Wipe the pan. In a small bowl, combine ¼ teaspoon salt, 1/8 teaspoon pepper, and four eggs. Whisk gently.
Heat the pan over medium heat. Add 1 ½ teaspoons of butter and the egg mixture. Cook for a minute, or until center begins to set but is still very soft.
Spread half of mushroom mixture at the center of the omelet. Sprinkle ¼ teaspoon salt and ¹⁄8 teaspoon pepper.
To loosen the omelet run a spatula around edges and under the omelet. Fold it in half.
Repeat procedure with remaining ingredients.
So are omelets healthy? Yes, if you reduce the oil used to fry them and consume them in moderation. They are an absolute treat with abundant nutrients to start your day. However, it is also important to exercise as it has many health benefits as well.
Related:
Sources:
Cousineau, R., “Open-Faced Pastrami Omelet on Pumpernickel,” MyRecipes, April 22, 2013; http://www.myrecipes.com/recipe/pastrami-omelet-pumpernickel.
Bonom, D., “Mushroom and Spinach Omelet,” MyRecipes, March 23, 2015; http://www.myrecipes.com/recipe/mushroom-spinach-omelet.
Cespedes, A., “NUTRITION OF A HARD-BOILED EGG VS. A FRIED EGG,” Live Well; http://livewell.jillianmichaels.com/nutrition-hardboiled-egg-vs-fried-egg-5552.html, last accessed April 17, 2017.
“Nutrition Guide for a Veggie Omelet,” SF Gate; http://healthyeating.sfgate.com/nutrition-guide-veggie-omelet-9009.html.
Rice, L., “Benefits of a High Protein Breakfast,” Fit Star, April 8, 2014; http://fitstar.com/benefits-high-protein-breakfast/