Vitamin D is critical for strong, healthy bones and is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps in the absorption of essential minerals like calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphate, and zinc. In this article, we will discuss vitamin D foods for vegetarians but before that let’s look at some other major sources of vitamin D.
The prime source of vitamin D is sunlight. It is not a direct source, but the UVB rays trigger vitamin D synthesis when they penetrate our skin. In addition, there are vitamin D-rich foods which should be included in meals regularly.
Non-vegetarians, especially fish lovers, have an easy access to vitamin D. But what about the vegetarians who don’t eat fish or meat? How can they get a regular and easy dose of vitamin D? Well, thankfully there are some vitamin D-rich foods for vegetarians as well.
Top 11 Vitamin D Foods for Vegetarians
It could be a tad challenging for vegetarians to obtain vitamin D daily, as most of the vitamin D-rich foods fall in the non-vegetarian food category.
Nevertheless, it’s not impossible for vegetarians to have strong bones because they can a opt for foods that are vitamin D-rich. Here are the top 11 vitamin D foods for vegetarians.
1. Soy products
Tofu is one of the best foods for vegetarians to take in a good amount of vitamin D. It is made from soy milk and is highly nutritious.
A serving of 79 grams of tofu offers 581 IU of vitamin D. Other soy products like plain soy milk and soy yogurt provide 338 IU and 161 IU of vitamin D, respectively, for a serving of one cup.
Dairy & Eggs-
2. Milk
Milk is a wholesome food that is rich in vitamin D as well as other nutrients. One glass of whole milk provides 20% DV of vitamin D.
The process of skimming of milk removes all fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamin D. Thus, these days, fortified milk is quite popular. Fortified milk is infused with fat-soluble vitamins A and D and forms a major part of the American diet.
3. Ricotta cheese
It is to be noted that only whole milk, and not its by-products like yogurt, cheese, and ice cream, contains a good quantity of vitamin D.
And then there is ricotta cheese—the only by-product of milk that has five times more vitamin D than other cheese. It is one of the best vitamin D foods for vegetarians. Each serving of ricotta cheese will give you 25 IU of vitamin D.
4. Butter
Another dairy product that could be a good source of vitamin D for vegetarians is butter. A cup of butter will provide 32% DV of vitamin D.
5. Eggs
Eggs are also a good source of vitamin D. One whole hard-boiled egg will give you 41 IU of vitamin D. Duck and goose eggs are comparatively more nutritious and healthier than chicken eggs.
Mushrooms-
6. Shiitake mushrooms
Mushrooms are a good plant source of nutrients. Shiitake mushrooms are a type of edible mushrooms that contain a good amount of iron, vitamin B complex, and vitamin D.
Inherently, these mushrooms provide only three percent DV of vitamin D, but if they are allowed to receive sufficient sunlight while growing, then there might be a significant increase in their vitamin D content.
Related: 5 Benefits of Vitamin D
7. White mushrooms
Commonly known as button mushrooms, white mushrooms are also a wonderful source of vitamin D. A cup of stir-fried white mushrooms will provide a moderate amount of the vitamin. They contain 22.7 IU which works out to six percent DV of vitamin D.
Cereals-
8. Fortified Cereals
Certain types of cereals contain a fair amount of vitamin D. Many bran cereals offer 131 IU of vitamin D, while cereals fortified with fruits provide 11 IU of vitamin D. It is recommended to buy cereals that contain at least 100 IU of vitamin D.
9. Oatmeal
Oatmeal is a wholesome breakfast food, and is also fortified with vitamin D. Fiber-rich (packaged) oatmeal can provide about 25% DV of vitamin D.
10. Fortified orange juice
Citrus fruits like oranges are a rich source of vitamin C and vitamin A. Fresh, homemade orange juice lacks vitamin D, however, certain brands of orange juice are fortified with vitamin D.
A one cup serving of packaged orange juice will provide at least 100 IU vitamin D. However, when buying packaged orange juice, be sure to check for sugar content, preservatives, and other additives.
11. Cod liver oil supplements
Cod liver oil is a popular supplement that contains high values of vitamin A, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids.
A 100-gram serving of cod liver oil provides 1,667% DV of vitamin D, while a tablespoon of 14 grams and five grams of the supplement will provide 227% and 75% DV of vitamin D respectively.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin D
Most Americans get their vitamin D from supplements and fortified milk. Here is the recommended dosage of vitamin D:
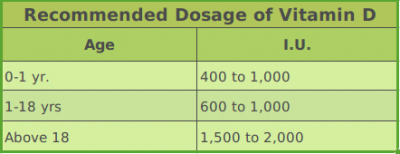
Individuals up to the age of one year should take 400 to 1,000 IU of vitamin D daily, those between age of one and 18 years should consume 600 to 1,000 IU of vitamin D, and all individuals above 18 years should have 1,500 to 2,000 IU of vitamin D daily. These optimum amounts of vitamin D can be easily obtained by consuming above vitamin D foods for vegetarians.
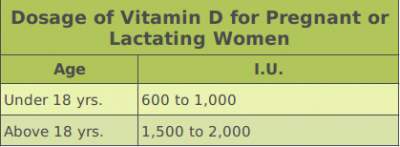
Pregnant or lactating women under 18 years should take a vitamin D dosage of 600 to 1,000 IU daily. Pregnant or lactating women over 18 years of age should take 1,500 to 2,000 IU of vitamin D dosage daily.
Vitamin D along with calcium is extremely essential to prevent osteoporosis. Women especially need to monitor their calcium and vitamin D3 levels, and need to consult a doctor if their levels are low.
What Can Vitamin D Toxicity Lead To?
An excessive intake of vitamin D-rich foods, be it vegetarian or non-vegetarian, causes vitamin D toxicity in the body.
Vitamin D toxicity occurs when there is an excess of vitamin D in the body. This condition is called hypervitaminosis D, a rare but potentially serious condition in the body.
Hypervitaminosis D is usually caused by an overdose of vitamin D through supplements. Large amounts of vitamin D, say 40,000 IU per day for a couple of months or longer, could be harmful to health. Since vitamin D is a fat-soluble nutrient, our body takes a long time to process it.
Large doses of vitamin D cause the liver to produce greater amounts of a chemical called 25(OH)D. High amounts of 25(OH)D cause excess absorption of calcium in the bloodstream, leading to high blood calcium condition known as hypercalcemia.
The symptoms of hypercalcemia include feeling nauseated, nausea, poor appetite or loss of appetite, feeling very thirsty, frequent urination, constipation or diarrhea, abdominal pain, muscle pain or weakness, bone pain, kidney problems, and fatigue.
The treatment for hypercalcemia is discontinued use of vitamin D supplements. In severe cases, medical intervention is recommended, and prescribed medications include corticosteroids or bisphosphonates. Patients with kidney or liver problems are more likely to suffer from vitamin D toxicity.
How Vitamin D Deficiency Can Affect You?
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient which is required in adequate amounts for proper calcium and phosphorus absorption. It helps in the development and maintenance of healthy bones and teeth.
The body requires two types of vitamin D─D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). Medical studies have suggested that vitamin D is vital to prevent diseases and conditions that include cancer, type 1 diabetes, and multiple sclerosis.
A deficiency of vitamin D can cause rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. Vegetarians can prevent these deficiencies by consuming above vitamin D rich foods.
Technically speaking, vitamin D is considered a pro-hormone in the medical world. This is because our body is capable of generating vitamin D when there is direct contact of sunlight with it.
In addition to promoting healthy and stronger bones, vitamin D supports brain and cardiovascular health, too. It improves the immune and nervous systems, helps with normal liver function, and aids in cancer treatment as well.
Related:
Sources:
“Vitamin D and the Immune System,” National Center for Biotechnology Information; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3166406/, last accessed March 27, 2017.
DeNoon, D., “New Guidelines Suggest Higher Doses of Vitamin D,” WebMD, June 6, 2011; http://www.webmd.com/diet/news/20110606/new-guidelines-suggest-higher-doses-of-vitamin-d#2, last accessed March 27, 2017
Zeratsky, K., “What is vitamin D toxicity, and should I worry about it since I take supplements?” Mayo Clinic, February 5, 2015; http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/vitamin-d-toxicity/faq-20058108, last accessed March 27, 2017.
“Am I getting too much vitamin D?” Vitamin D Council; https://www.vitamindcouncil.org/about-vitamin-d/am-i-getting-too-much-vitamin-d/, last accessed March 27, 2017